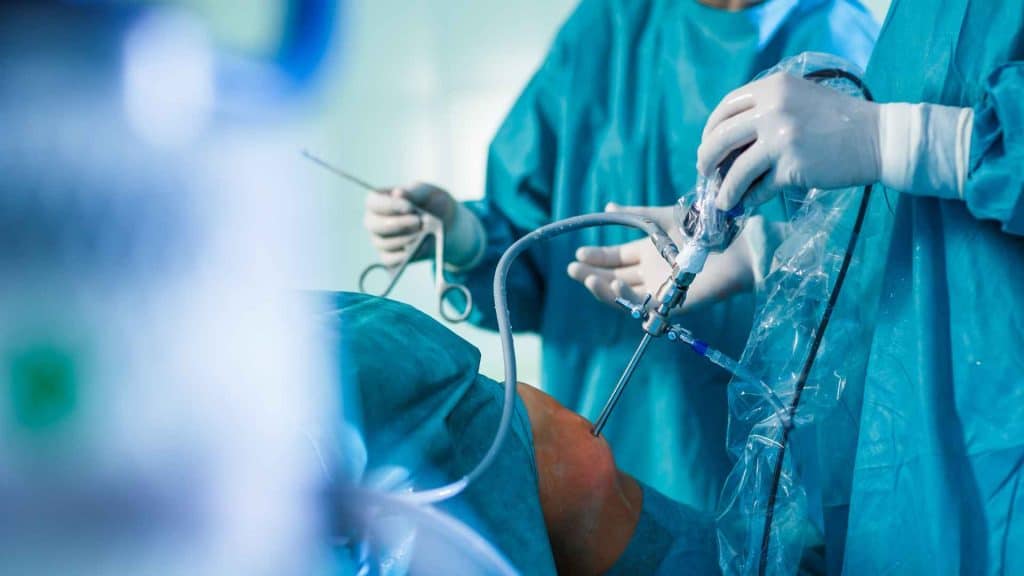
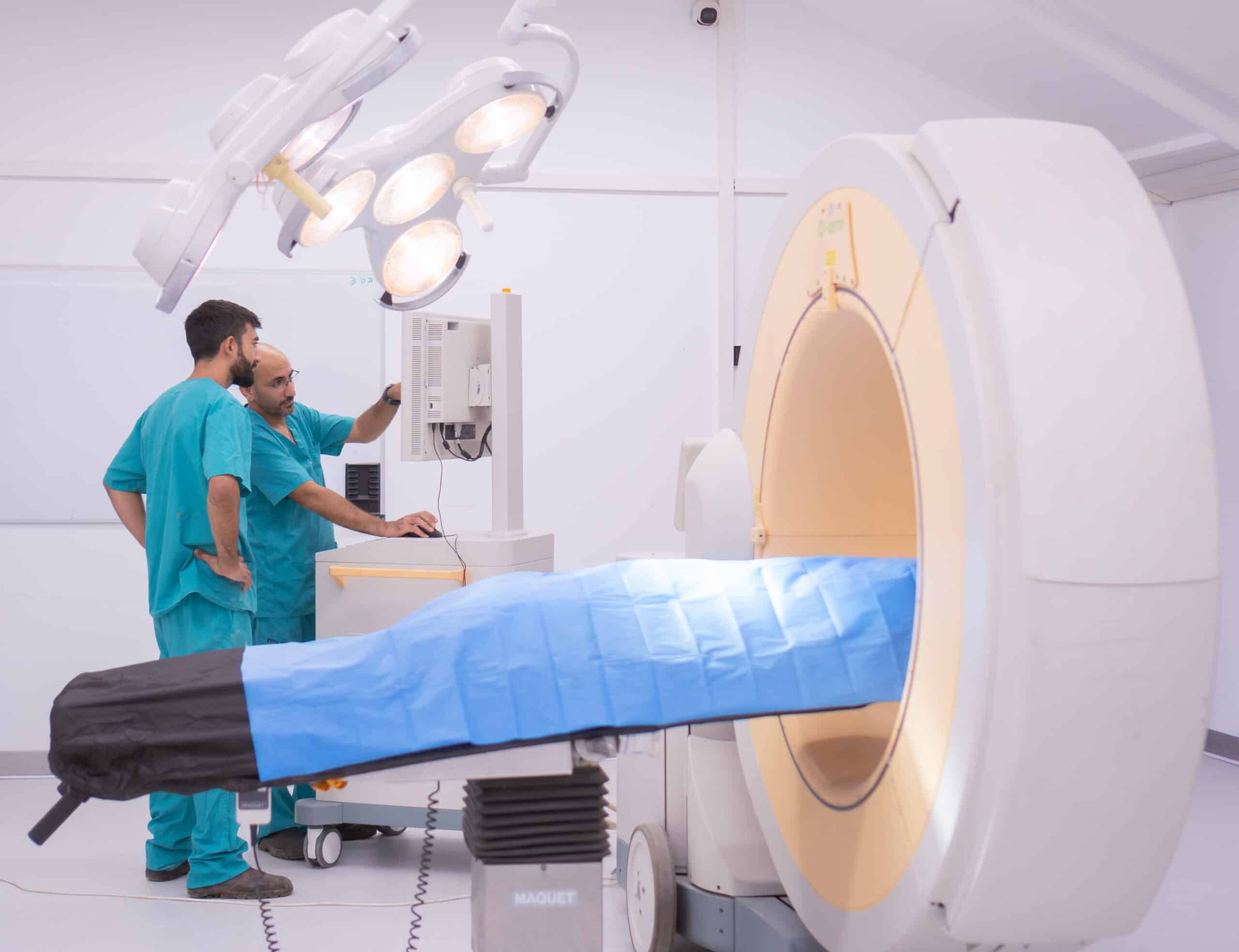
The development of tools for conducting special orthopedic surgeries such as spinal cord surgeries involves working with spine samples that are provided fresh or frozen. Medical devices for treating bone defects and models of osteitis for pharmaceuticals and formulations development are readily available including the collaboration with a biological laboratory qualified for the determination of efficacy. Surgery room dedicated tools are available for providing excellent precision, high image quality and operability.
In the rapidly advancing field of orthopedics, medical devices play a pivotal role in patient care. But, before these devices can be used, they must undergo a rigorous certification process to ensure safety and efficacy. The journey to certification is a critical step for manufacturers and healthcare providers alike.
Exploring the complex world of regulatory standards is no small feat. Orthopedic medical devices certification demands a thorough understanding of the guidelines and a meticulous approach to compliance. It’s a process that underscores the commitment to patient health and quality innovation in the field.
As technology evolves, so do the requirements for certification. Staying abreast of the latest developments is essential for those looking to bring new orthopedic solutions to market. Let’s investigate into the intricacies of obtaining certification and what it means for the future of orthopedic care.
Understanding Orthopedic Medical Devices Certification
The pathway to orthopedic medical devices certification is complex, requiring compliance with rigorous standards to ensure the safety and effectiveness of devices intended for human use. It’s a multistep process involving both manufacturers and regulatory bodies, each with critical roles to play.
Manufacturers must design and develop products in line with stringent regulations that encompass materials, design, and manufacturing processes. At Biotech Farm Ltd., the development of orthopedic medical devices takes center stage, often utilizing large animals like pigs, sheep, and calves to conduct pre-regulatory studies and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) validation studies. Their advanced facilities and professional crew support the intricate phases of device development with an eye toward certification requirements.
| Biotech Farm Ltd. | Orthopedic Research Focus |
| Animal Models | Pigs, Sheep, Calves |
| Applications | Bone Regeneration, Orthopedic Device Testing |
Every device intended for orthopedic use must go through extensive pre-clinical testing before entering the GCP validation stage. Certification not only underscores a device’s safety but also its efficacy in treatment. With conditions like diabetes and postoperative support following colon cancer surgeries becoming more prevalent, the application of certified medical devices is critical.
The regulatory world for orthopedic medical device certification is ever-changing, adapting to new technologies and scientific advancements. Biotech Farm’s emphasis on state-of-the-art research and thorough pre-clinical studies aligns with the evolving nature of certification criteria, aiming to fulfill the highest industry standards. As it stands, there’s an unyielding commitment to bridging the gap between innovation and patient safety—where obtaining certification is merely one piece of the complex puzzle in the orthopedic medical device lifecycle.
Importance of Certification in Orthopedic Care
The journey towards achieving orthopedic medical devices certification represents a critical juncture in the development and eventual deployment of these devices in clinical settings. The stamp of approval from regulatory authorities assures healthcare providers and patients alike that these devices meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
Certification acts as a safeguard, highlighting that devices have undergone extensive testing and validation to meet specific standards. It operates under the premise that orthopedic devices, which are often implanted into the human body, carry significant risks if they fail to perform as intended. Without certification, patients could be subjected to devices plagued by malfunction, leading to dire consequences including increased pain, immobility, and even additional surgeries.
Manufacturers like Biotech Farm Ltd. must navigate complex pre-clinical stages, which include large animal studies, and adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) validation studies. These steps are not only pivotal for meeting the regulatory requirements but also for refining the device’s design and functionality—safeguarding the patients’ well-being.
With orthopedic ailments on the rise due to an aging population and increased physical activity, the demand for medical devices in this area is escalating. Certification not only confirms reliability but also plays a role in the competitive edge of a product. In a market flooded with alternatives, certified devices stand out to surgeons and hospitals as the preferred choice, primarily due to the guaranteed quality and safety.
Besides, certification processes are ever-evolving, with regulatory bodies continuously updating criteria to incorporate the latest in scientific research and technological advancements. This ongoing development ensures that orthopedic medical devices remain on the cutting edge, delivering optimal treatment outcomes and staying aligned with current medical standards.
Through careful monitoring and strict adherence to regulatory directives, companies like Biotech Farm Ltd. are instrumental in ensuring that the journey from concept to certified device is thorough and uncompromising in quality. Their commitment serves the dual purpose of fostering innovation while steadfastly protecting the health and safety of patients.
The Certification Process for Orthopedic Medical Devices
Orthopedic medical devices undergo a rigorous certification process to meet industry standards and regulatory requirements. The certification process is multifaceted, designed to ensure devices are safe for use and effective in their intended applications.
Step-by-Step Certification Roadmap
Entities such as Biotech Farm Ltd. follow a structured roadmap to navigate the certification world:
- Preclinical Studies: Initial testing often involves preclinical studies on large animals to assess the basic safety and functionality of a device.
- Application for Certification: The manufacturing company submits an application to the appropriate regulatory body, detailing the device and its intended use.
- Review of Technical Documentation: A thorough review of technical documentation that supports the safety and effectiveness of the orthopedic device takes place.
- Quality Management System (QMS) Assessment: Certification bodies audit the manufacturer’s QMS to ensure compliance with industry standards like ISO 13485.
- Clinical Evaluation: Sometimes involving human trials or simulations, clinical evaluations provide additional data on the device’s performance.
- Inspections: Regulatory agencies may require inspections of manufacturing facilities to verify adherence to production standards and protocols.
Key Certification Standards
Orthopedic medical devices certification revolves around crucial standards:
- ISO 13485: This standard defines requirements for a comprehensive QMS in the design and manufacture of medical devices.
- FDA Regulations: In the US, the Food and Drug Administration mandates that devices comply with specific regulations, which may include Premarket Approval (PMA) or 510(k) clearance.
- CE Marking: In Europe, obtaining a CE mark indicates that a device meets the EU’s health, safety, and environmental protection directives.
The evolution of orthopedic devices continues to push the boundaries of traditional certification pathways. Innovations require an adaptive approach to certification that keeps pace with technological advancements. Meanwhile, companies like Biotech Farm Ltd. invest in the development and validation of devices, adhering to the stringent standards set forth by regulatory authorities. This commitment ensures every step of the certification process not only secures the necessary approvals but also upholds the highest level of patient safety and device performance.
Key Guidelines for Certification
When it comes to orthopedic medical devices certification, adhering to specific guidelines is crucial for successfully exploring the complex process. First and foremost, manufacturers must ensure comprehensive documentation of the device’s design and development. This includes a detailed description of the device’s intended use, design specifications, and manufacturing processes. Documentation plays a pivotal role in demonstrating compliance with regulatory standards.
The next essential step involves rigorous preclinical testing. These tests, which often take place at specialized facilities like Biotech Farm Ltd., assess the device’s performance in conditions that mimic its intended use. The suitability of Biotech Farm’s facilities for large animals, such as pigs, sheep, and calves, makes it a valuable asset for conducting these critical evaluations.
Manufacturers must also establish a robust Quality Management System (QMS) in line with ISO 13485 standards. A thorough QMS assessment ensures the consistency and safety of the device throughout its lifecycle. Compliance with this standard demonstrates that the manufacturer has effectively implemented a framework for continuous improvement, risk management, and process validation.
Clinical evaluation is another cornerstone of the certification process. This involves the compilation and assessment of clinical data to confirm the clinical safety and performance of the orthopedic device. Evidence from clinical evaluations supports the application for certification and may vary depending on the regulatory region.
Besides, companies like Biotech Farm Ltd. must meet specific monitoring and post-market surveillance requirements. This ongoing process includes the collection and analysis of data about the use of the device after it has entered the market. It ensures that any potential risks are identified and addressed promptly.
It’s also important to recognize that orthopedic medical devices certification is not static. It must be adaptive to stay in tune with technological advancements and emerging industry trends. This dynamism reflects the commitment of companies to uphold regulatory standards and prioritize patient safety. Manufacturers are expected to stay abreast of changes in regulations and make necessary adjustments to maintain certification status.
Biotech Farm Ltd., with its focus on both animal and human health and its state-of-the-art facilities, exemplifies the dedication to advancing medical device R&D through rigorous and scientifically supported pre-regulatory studies. Through adherence to these key guidelines, manufacturers aim to navigate the certification process successfully, ensuring that orthopedic devices meet the highest standards for safety and performance before reaching the market.
Staying Updated on Certification Requirements
Keeping abreast of Certification Requirements for orthopedic medical devices is crucial for manufacturers to maintain compliance and market access. Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, are constantly updating their standards and guidelines to reflect new research findings, and technological advancements. Biotech Farm Ltd., with its commitment to excellence understands that staying informed is essential for the success of their devices throughout their lifecycle.
For manufacturers focused on Orthopedic Medical Devices Certification, it’s essential they monitor changes in the regulatory environment. Key strategies include:
- Subscribing to industry newsletters and regulatory updates
- Participating in relevant workshops, seminars, and webinars
- Engaging with professional regulatory consultants
One must also stay current with literature on emerging technologies and clinical practices. This includes:
- Regularly reviewing new research in orthopedics
- Attending industry conferences
- Networking with peers
At Biotech Farm Ltd., adherence to current requirements is ensured through an internal review process that frequently assesses the regulatory world. This involves an interdisciplinary team approach integrating Legal, Clinical, and Regulatory Affairs experts to dissect new regulations and carry out necessary changes swiftly.
Manufacturers must also prepare for the prospect of revised guidance or newly introduced regulations affecting their devices. This proactive stance enables them to pivot their strategies effectively, ensuring continuous compliance.
Adoption of an electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) has proven advantageous for many manufacturers. An eQMS can offer real-time updates on regulatory changes, align existing standards with new policies, and automate certain documentation processes.
Finally, active membership in trade associations and regulatory committees allows companies like Biotech Farm Ltd. to not only stay informed but also to contribute to the development of future standards and guidelines. This proactive involvement can provide strategic advantages, such as early insights into forthcoming regulatory trends and the opportunity to shape discussions around certification processes.
Conclusion
Exploring the intricate world of orthopedic medical device certification demands vigilance and a proactive approach. Manufacturers must embrace the evolving nature of regulations and quality management to uphold the highest standards of device safety and efficacy. By integrating an eQMS and engaging actively with industry peers and regulatory bodies, companies can foster a culture of excellence and trust. Biotech Farm Ltd.’s commitment serves as a beacon for others in the industry, underscoring the critical role of compliance in advancing healthcare and patient outcomes.
פיתוח מכשור רפואי אורטופדי
פיתוח כלים אשר יעזרו בביצוע ניתוחים אורטופדיים מיוחדים כגון ניתוחים בעמוד השדרה דורשים עבודה עם עמודי שדרה לדוגמה אשר מסופקים טריים או מוקפאים.
בנוסף חוות ביוטק מספקת:
מכשור רפואי לטיפול בפגמים בעמוד השדרה.
מודלים של אוסטאיטיס לפיתוח תרופות הזמינים בקלות.
שיתוף פעולה עם מעבדה ביולוגית המוסמכת לבדיקת יעילות.
חדרי הניתוח מצויידים במיכשור ייעודי כולל מכשירי שיקוף מתקדמים ברזולוציה גבוהה המספקים דיוק מירבי, איכות צילום ושיקוף גבוהה, קלות בתפעול ונוחות בשימוש.